전송 게이트가 내장된 Gate/Body-Tied P-Channel Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 감도 가변형 능동 화소 센서
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
In this study, the sensitivity of an active pixel sensor (APS) was adjusted by employing a gate/body-tied (GBT) p-channel metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (PMOSFET)-type photodetector with a transfer gate. A GBT PMOSFET-type photodetector can amplify the photocurrent generated by light. Consequently, APSs that incorporate GBT PMOSFET-type photodetectors are more sensitive than those APSs that are based on p-n junctions. In this study, a transfer gate was added to the conventional GBT PMOSFETtype photodetector. Such a photodetector can adjust the sensitivity of the APS by controlling the amount of charge transmitted from the drain to the floating diffusion node according to the voltage of the transfer gate. The results obtained from conducted simulations and measurements corroborate that, the sensitivity of an APS, which incorporates a GBT PMOSFET-type photodetector with a built-in transfer gate, can be adjusted according to the voltage of the transfer gate. Furthermore, the chip was fabricated by employing the standard 0.35 μm complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology, and the variable sensitivity of the APS was thereby experimentally verified.
Keywords:
Transfer gate, Active pixel sensor, Gate/body-tied, Photodetector, PMOSFET, Adjustable sensitivity1. 서 론
이미지 센서는 광학 렌즈를 통해 들어온 빛을 광전효과를 이용하여 디지털 신호로 변환하는 반도체 센서이다. 최근, 이미지 센서는 휴대전화, 무인감시 카메라, 산업용 카메라 등 다양한 산업 분야에 이용되고 있으며 관련 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다. 이에 따라 이미지 센서의 중요성이 대두되고 있다[1–4]. 그 중 주요 연구 분야로는 이미지 센서의 광 검출기 분야가 있다. 이미지 센서에 사용되는 광 검출기는 p-n 접합 형 광 검출기, MOSFET형 광 검출기, pinned photodiode (PPD)형 광 검출기, bipolar junction transistor (BJTs) 광 검출기 등이 있다[5-8]. 특히 gate / body-tied (GBT) p-channel MOSFET (PMOSFET) 구조 광 검출기는 빛에 의해 생성되는 광 전류를 증폭하기 때문에 적은 빛에서도 신호 전하가 빠르게 포화가 되어 고감도 특성을 가진다[9-12].
본 논문에서는 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서를 시뮬레이션과 측정을 통해 감도가 가변되는 것을 확인하였다. 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기는 적은 빛으로도 고감도의 특성을 가진다. 이러한 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기에 전송 게이트를 내장하여 전송 게이트의 전압에 따라 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 드레인에서 FD노드로 이동하는 전하량을 제어하여 능동 화소 센서의 감도를 가변 한다. 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서는 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 고감도 특성과 전송 게이트의 전압에 따라 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 드레인에서 FD 노드로 이동하는 전하량을 제어하는 기능을 사용하여 낮은 조도에서도 고감도 상태를 유지하고, 높은 조도에서는 낮은 감도로 조절이 가능하다.
전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 감도 가변형 능동 화소 센서는 2-poly 4-metal 0.35 μm표준CMOS 공정을 사용하여 설계 및 제조되었으며, 능동 화소 센서의 측정 결과는 Cadence tool을 이용한 시뮬레이션 결과와 비교되었다.
2. 동작 원리
2.1 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기
Fig. 1(a) 는 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 기호를 나타낸다. 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기는 바디 노드와 게이트 노드가 물리적으로 묶여서 설계된다. Fig. 1 (b)는 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기에 전송 게이트 MOSFET이 연결된 구조를 나타낸다. Fig. 1 (c) 는 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 기호를 나타낸다. 전송게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기는 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 드레인과 전송 게이트의 소스가 연결되어있으며, 바디도 함께 묶여있다.
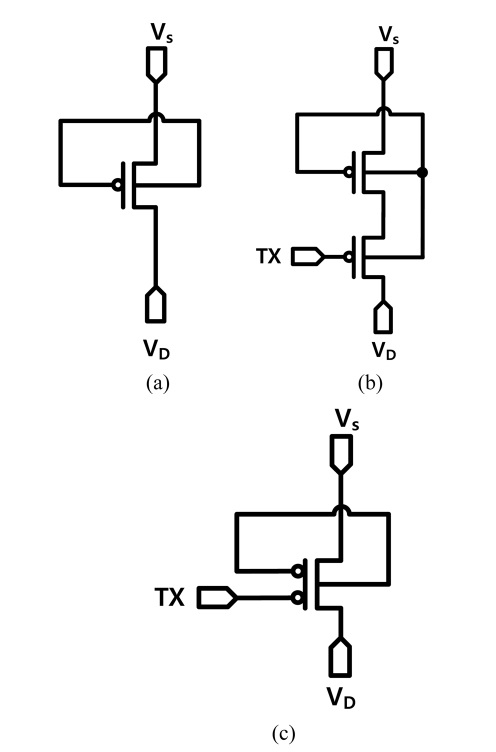
(a) Symbol of conventional GBT PMOSFET-type photodetector, (b) schematic of conventional GBT PMOSFET-type photodetector with transfer gate and (c) symbol of conventional GBT PMOSFET-type photodetector with transfer gate.
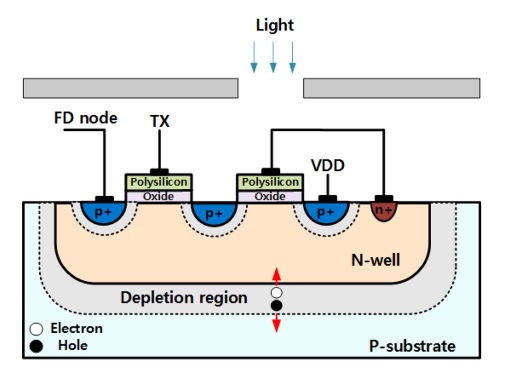
Fig. 2는 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 단면도를 나타낸다. 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기는 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기와 내장된 전송 게이트는 n-well을 공유하도록 설계되었다. 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기는 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 게이트를 제외한 영역은 금속선으로 차폐되어 있다. 따라서 빛은 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조광 검출기의 게이트 영역에만 입사된다. 입사되는 빛은 n-well과 p 기판 사이에 공핍 영역과 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광검출기의 드레인 및 소스 영역 사이의 공핍 영역에서 전자 정공 쌍을 형성한다. N-well과 p 기판 사이의 공핍 영역에서 형성되는 전자 정공 쌍은 전자는 n-well로 이동하고 정공은 p 기판으로 이동한다. 입사하는 빛에 의해 생성되는 전자는 n-well에 축적되고, n-well은 축적된 전자에 의해 전압이 낮아지게 되고 n-well과 물리적으로 묶여져 있는 게이트의 전압도 함께 낮아진다. 또한, 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 p+영역과 n-well 사이의 공핍 영역에서 생성된 전자 정공 쌍은 전자는 nwell로 이동하여 축적되고, 정공은 정공의 전위 장벽이 낮은 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 채널을 통해 이동한다. 전송 게이트의 전압을 가변 하여 채널을 통해 흐르는 전류의 양을 제어한다. 기존의 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 사용하는 능동 화소 센서는 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 흐르는 전류를 제어할 수 없다. 그러나 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용하는 능동 화소 센서는 전송 게이트의 전압을 조정하여 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 흐르는 전류를 제어할 수 있다.
2.2 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기 능동 화소 센서 구현
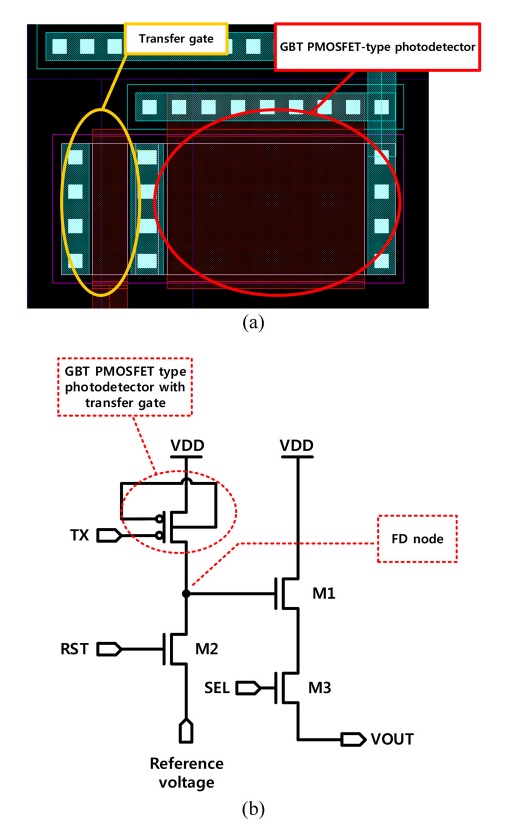
Fig. 3(a) 는 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 레이아웃을 나타낸다. 광 검출기의 영역은 3.8 × 5.7 μm2 이다. Fig. 3(b) 는 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서의 회로도를 나타낸다. 전송 게이트를 내장한 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서 구조는 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSPET 구조 광 검출기와 3개의 n-channel MOSFET (NMOSFET)으로 구성된다. NMOSFET중 M1트랜지스터는 소스 팔로워 역할로써 FD 노드의 전압을 증폭시키는 역할을 하며, M2 트랜지스터는 리셋 트랜지스터로써 FD 노드의 신호 전압을 기준 전압으로 초기화하는 동작을 한다. 그리고 M3 트랜지스터는 선택 트랜지스터로 증폭된 FD 노드의 전압을 능동 화소 센서의 출력 노드에 연결시키는 동작을 수행한다.
3. 결과 및 고찰
Fig. 4(a) 는 빛이 꺼져있을 때 광 검출기의 전류 측정을 위해 프로브 스테이션을 사용하는 실험 환경을 나타낸다. Fig. 4(b)는 빛이 켜져 있을 때 광 검출기의 전류 측정을 위해 프로브 스테이션을 사용하는 실험 환경을 나타낸다. 프로브 스테이션은 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET구조 광 검출기에 흐르는 전류를 측정하는데 사용되었다. 사용된 프로브 스테이션에는 총 4개의 프로브가 있으며 각 프로브는 PMOSFET의 드레인, PMOSFET의 소스, 전송 게이트 및 접지에 연결된다. 측정에 사용되는 프로브 스테이션은 광도를 조정할 수 있다.
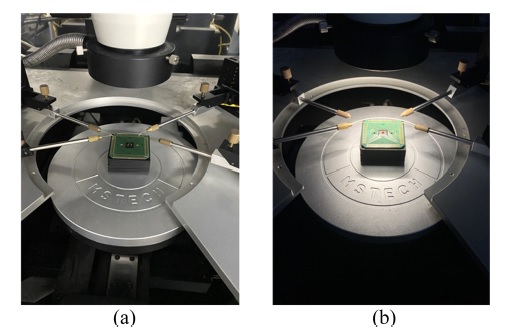
Experimental environment using probe station for current measurement of the photodetector (a) when light is off and (b) when light is on.
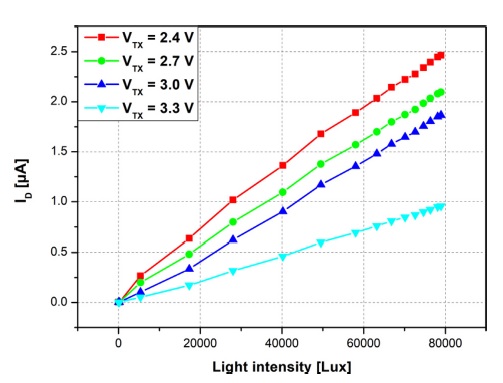
Fig. 5 는 광도의 함수로 VTX를 조정한 전류 측정 결과를 보여준다. VTX감소함에 따라 그래프의 기울기는 증가한다. 즉, 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기의 채널을 통해 흐르는 전류는 전송 게이트의 VTX를 제어하여 가변 된다. 따라서 광 검출기의 감도는 전송 게이트의 전압이 증가함에 따라 감소하는 것을 알 수 있다.
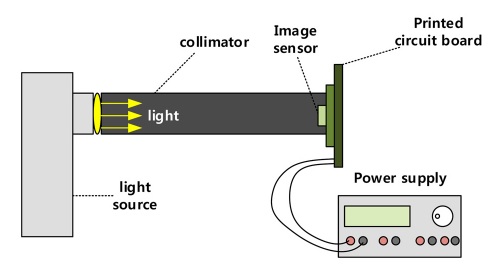
Fig. 6 은 photon transfer curve (PTC) 의 측정을 위해 광원과 전원 공급기를 사용하는 측정환경을 나타낸다.
Fig. 7(a) 는 PTC시뮬레이션 결과를 나타내고, Fig. 7(b) 는 PTC 측정 결과를 나타낸다. 시뮬레이션 및 측정 조건은 VREF: 1.0 V, VBias: 1.2 V, integration time: 500 μs를 사용하여 수행되었다. 시뮬레이션 결과와 측정 결과 모두 VTX 값이 증가함에 따라 능동 화소 센서의 감도가 감소함을 보여준다. 전송 게이트의 전압이 증가하면 전송 게이트 아래에서 정공의 채널 장벽의 높이가 증가한다. 따라서 FD 노드에 축적되는 정공의 양이 감소하고 능동 화소 센서의 감도가 감소한다.
(a) Simulation results of the photon transfer curve and (b) measurement results of the photon transfer curve.
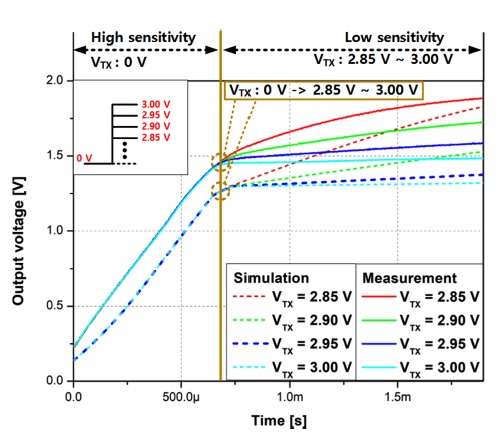
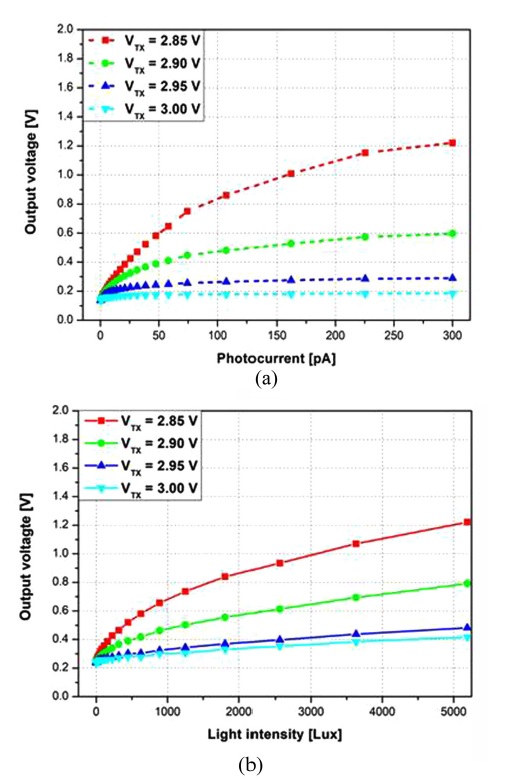
본 연구에서는 전송 게이트 전압(VTX)의 DC 레벨을 조절하므로써, 펄스 폭을 조절하는 방식보다 좀 더 손쉽게 능동 화소 센서의 출력 전압의 기울기 및 감도를 제어하는 방법을 사용하였다[13]. Fig. 8은 VTX 레벨에 따른 능동 화소 센서 구조의 출력 전압 시뮬레이션 결과와 VTX 레벨에 따른 능동 화소 센서 구조의 출력 전압 측정 결과를 나타낸다. 본 시뮬레이션과 측정에서 VTX의 레벨을 2.85 V에서 3.00 V까지 가변하였다. VTX의 레벨이 2.85 V에서 3.00 V로 변함에 따라 능동 화소 센서의 출력 전압의 기울기가 감소한다. 따라서 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서는 전송 게이트의 펄스 레벨이 증가함에 따라 능동 화소 센서의 출력 전압의 포화되는 시간이 느려지게 되고, 낮은 감도에서도 동작할 수 있는 것을 시뮬레이션과 측정을 통해 확인하였다.
4. 결 론
전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 감도 가변형 광 검출기 특성을 시뮬레이션과 측정을 통해 확인하였다. 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서의 감도는 전송 게이트의 전압이 증가함에 따라 낮아지는 것을 시뮬레이션과 측정을 통해 확인하였다. 결과적으로 감도 가변형 특성을 이용하여 전송 게이트가 내장된 GBT PMOSFET 구조 광 검출기를 이용한 감도 가변형 광 검출기를 이용한 능동 화소 센서는 전송 게이트에 인가되는 전압을 조절함에 따라 저조도에서는 고감도, 고조도에서는 저감도로 동작함을 시뮬레이션과 측정을 통해 확인하였다.
Acknowledgments
본 논문은 삼성전자 및 Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2018R1D1A3B0704995213) 와 Integrated Circuit Design Education Center (IDEC)의 지원에 의해 연구되 었다.
REFERENCES
-
R. H. Nixon, S. E. Kemeny, B. Pain, C. O. Staller, and E. R. Fossum, “256 × 256 CMOS active pixel sensor cameraon-a-chip”, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, Vol. 31, No. 12, pp. 2046–2050, 1996.
[https://doi.org/10.1109/4.545830]
-
E. R. Fossum, “CMOS image sensors: electronic cameraon-a-chip”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, Vol. 44, No. 10, pp. 1689–1698, 1997.
[https://doi.org/10.1109/16.628824]
-
M. Bigas, E. Cabruja, J. Forest, and J. Salvi, “Review of CMOS image sensors”, Microelectronics J., Vol. 37, No. 5, pp. 433–451, 2006.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2005.07.002]
-
S. H. Kim, H. Kwen, J. Jang, Y. M. Kim, and J. K. Shin, “2500 fps High-Speed Binary CMOS Image Sensor Using Gate/Body-Tied Type High-Sensitivity Photodetector,” J. Sens. Sci. Technol., Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 61–65, 2021.
[https://doi.org/10.46670/JSST.2021.30.1.61]
-
H. Alaibakhsh and M. A. Karami, “Analytical Modeling of Pinning Process in Pinned Photodiodes”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, Vol. 65, No. 10, pp. 4262–4368, 2018.
[https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2862251]
- J. H. Park, H. Kim, I. S. Wang, and J. K. Shin, “Quantumwired MOSFET photodetector fabricated by conventional photolithography on SOI substrate”, 2004 4th IEEE Conf. Nanotechnol., pp. 425–427, Munich, Germany, 2004.
-
E. R. Fossum and D. B. Hondongwa, “A review of the pinned photodiode for CCD and CMOS image sensors”, IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc., Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 33–43, 2014.
[https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2014.2306412]
-
L. A. P. Santos, G. G. Araujo, F. L. Oliveira, E. F. Silva, and M. A. P. Santos, “An alternative method for using bipolar junction transistors as a radiation dosimetry detector in breast cancer treatment”, Radiat. Meas., Vol. 71, pp. 407– 411, 2014.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2014.08.003]
- S. H. Seo, K. D. Kim, M. W. Seo, J. S. Kong, J. K. Shin, and P. Choi, “Optical characteristics of an N-Well/gate-tied PMOSFET-type photodetector with built-in transfer gate for CMOS image sensor”, Sensors Mater., Vol. 19, No. 7, pp. 435–444, 2007.
-
W. Zhang and M. Chan, “A high gain N-Well/Gate tied PMOSFET image sensor fabricated from a standard CMOS process”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, Vol. 48, No. 6, pp. 1097–1102, 2001.
[https://doi.org/10.1109/16.925233]
- F. Assaderaghil, D. Sinisky, S. Park, P. K. Ko, and C. Hu, “High Responsivity Photo-Sen”, pp. 149–150, 1998.
-
B. S. Choi, S. H. Kim, J. Lee, C. W. Oh, S. H. Seo, and J. K. Shin, “Complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor using gate/body-tied P-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor-type photodetector for high-speed binary operation”, Sensors Mater., Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 129–134, 2018.
[https://doi.org/10.18494/SAM.2018.1643]
-
S. H. Seo, S. H. Lee, M. Y. Do, J. K. Shin, and P. Choi, “Highly and Variably Sensitive Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Active Pixel Sensor Using P-Channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor-Type Photodetector with Transfer Gate”, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 45, No. 4B, 3470-3474, 2006.
[https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.45.3470]